What is Java?
Java is a high-level, general-purpose, object-oriented, and secure programming language developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems, Inc. in 1991.
Features of Java
- Simple: Java is a simple language because its syntax is simple, clean, and easy to understand. Complex and ambiguous concepts of C++ are either eliminated or re-implemented in Java. For example, pointer and operator overloading are not used in Java.
- Object-Oriented: In Java, everything is in the form of the object. It means it has some data and behavior. A program must have at least one class and object.
- Robust: Java makes an effort to check error at run time and compile time. It uses a strong memory management system called garbage collector. Exception handling and garbage collection features make it strong.
- Secure: Java is a secure programming language because it has no explicit pointer and programs runs in the virtual machine. Java contains a security manager that defines the access of Java classes.
- Platform-Independent: Java provides a guarantee that code writes once and run anywhere. This byte code is platform-independent and can be run on any machine.
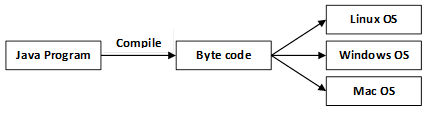
- Portable: Java Byte code can be carried to any platform. No implementation-dependent features. Everything related to storage is predefined, for example, the size of primitive data types.
- High Performance: Java is an interpreted language. Java enables high performance with the use of the Just-In-Time compiler.
- Distributed: Java also has networking facilities. It is designed for the distributed environment of the internet because it supports TCP/IP protocol. It can run over the internet. EJB and RMI are used to create a distributed system.
- Multi-threaded: Java also supports multi-threading. It means to handle more than one job a time.
Java "Hello, World!" Program
// Your First Program
class Tech Ocean{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}Output
Hello, World!
Comments
Post a Comment